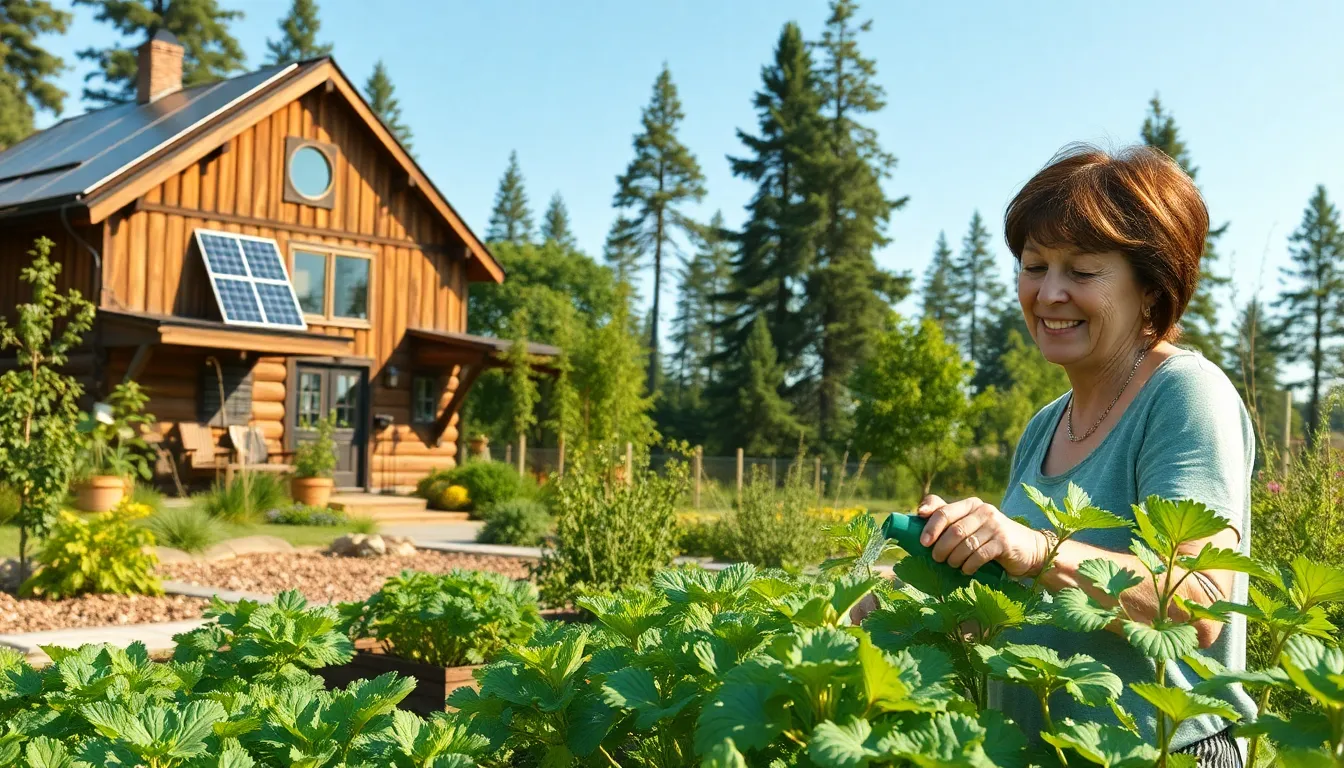
Imagine waking up to the sound of chirping birds instead of a blaring alarm clock. Off-grid homes offer the chance to ditch the daily grind and embrace a simpler, more sustainable lifestyle. With the right setup, anyone can live in harmony with nature while enjoying the comforts of modern living.
These homes aren’t just about being eco-friendly; they’re about freedom. Picture yourself sipping coffee on your porch, knowing your energy comes from the sun and your water from a nearby stream. Who needs a power company when you can be your own energy provider? Off-grid living is not just a trend; it’s a movement that empowers individuals to take control of their lives and reduce their carbon footprint—all while having a little fun along the way.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Off Grid Homes
Off-grid homes operate independently from public utilities. Individuals living in these homes utilize renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power for their electricity needs. Rainwater harvesting and water filtration systems often provide potable water. A self-sufficient lifestyle becomes achievable with gardening and permaculture practices, ensuring access to food without dependence on commercial systems.
Sustainability remains a core principle of off-grid living. These homes encourage reduced energy consumption through efficient designs and practices. Energy-efficient appliances and proper insulation help minimize energy needs. Building materials are often sourced sustainably, further supporting eco-friendly goals.
Residents enjoy privacy and seclusion with off-grid homes, often located far from urban areas. This distance fosters a strong connection to nature, enhancing mental well-being. People frequently experience reduced stress and improved quality of life in tranquil settings.
Challenges accompany off-grid living as well. Initial setup costs can be substantial, with solar panels, wind turbines, and state-of-the-art battery systems. Maintenance of systems requires knowledge and dedication to ensure long-term functionality. Weather conditions also impact energy production, affecting reliability.
Technological advancements now simplify off-grid living. Smart home technologies and energy management systems optimize resource use. Individuals leverage apps and software for monitoring systems, making life easier in remote locations.
Overall, off-grid homes provide a compelling alternative to traditional living. They not only promote self-sufficiency but also reduce environmental impact, aligning with modern sustainability standards.
Benefits of Off Grid Living

Off-grid living offers numerous advantages that appeal to many individuals looking for a change in lifestyle. These benefits include financial savings, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced quality of life.
Financial Savings
Residents of off-grid homes often experience significant cost reductions. Utilities like electricity and water often incur monthly fees that add up quickly. By harnessing renewable energy sources, individuals can eliminate or greatly reduce those expenses. Solar panels, wind turbines, and other technologies provide sustainable power without ongoing costs. Water collection systems facilitate access to clean water—further decreasing reliance on external providers. Additionally, off-grid living fosters self-sufficiency in food through gardening, which leads to savings on grocery bills. Overall, the combined effect of these measures contributes to a more economical lifestyle.
Environmental Impact
Off-grid living prioritizes sustainability and minimizes one’s carbon footprint. Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Utilizing rainwater harvesting systems conserves natural resources and lowers demand on municipal water supplies. Furthermore, off-grid homes often employ eco-friendly building materials and energy-efficient designs, promoting a healthier environment. A lifestyle focused on reusability and conservation helps preserve local ecosystems and wildlife. Ultimately, these efforts contribute to a more resilient planet for future generations.
Types of Off Grid Homes
Off-grid homes encompass various styles, each tailored to unique preferences and environments. Understanding these types helps individuals choose the right fit for their lifestyle.
Tiny Houses
Tiny houses offer a minimalist approach to off-grid living. Typically under 400 square feet, they maximize space efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Many homeowners utilize mobile tiny houses, allowing for flexibility in location. Solar panels power electrical needs, while composting toilets and rainwater systems promote self-sufficiency. These compact homes often encourage a simpler lifestyle, aligning with off-grid principles.
Earth Sheltered Homes
Earth sheltered homes blend seamlessly into their surroundings. Constructed partially underground, they possess excellent thermal properties, which reduce energy consumption. Natural insulation from soil minimizes heating and cooling demands. Often, these homes incorporate passive solar design, capitalizing on sunlight while maintaining privacy. This style fosters harmony with nature and showcases sustainable living at its best.
Cabins and Yurts
Cabins and yurts enrich the off-grid experience through distinct architectural designs. Cabins often feature rustic aesthetics and sturdy materials, providing comfort in remote locations. Alternatively, yurts offer lightweight, portable structures, ideal for diverse terrains. Both options typically utilize renewable energy sources and efficient systems for heating and water collection. These homes promote a close connection to nature, enhancing off-grid living’s appeal.
Sustainable Living Practices
Sustainable living practices form the foundation of off-grid homes, enabling residents to thrive independently from conventional systems.
Renewable Energy Sources
Solar panels represent a primary renewable energy source. Wind turbines, installed strategically, harness wind power for electricity. Hydro power systems utilize flowing water to generate energy. Each method provides a clean, reliable power supply, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Residents often combine these systems for enhanced energy security. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, ensure electricity availability during cloudy days. Implementing energy-efficient appliances further decreases consumption and fosters sustainability. Overall, these renewable options empower off-grid residents to maintain a low carbon footprint.
Water Collection and Filtration
Rainwater harvesting systems collect water from rooftops, channeling it into storage tanks. This process minimizes reliance on municipal water sources. Filtration systems purify collected rainwater, making it safe for drinking and cooking. Various methods exist, including activated carbon filters and ultraviolet light purifiers. Techniques like gray water recycling enable households to reuse water for irrigation. Monitoring water usage proves essential in maximizing conservation efforts. With these systems in place, off-grid living encourages self-sufficiency in water supply.
Challenges of Off Grid Living
Off-grid living presents unique challenges that individuals must navigate when pursuing this lifestyle choice.
Initial Setup Costs
Initial setup costs for off-grid homes can be significant. Depending on the chosen location, an off-grid system can range from $15,000 to over $100,000. Factors influencing these costs include solar panels, batteries, wind turbines, and water system installations. Additionally, land purchase and site preparation contribute to the financial burden. Planning for these expenses before embarking on an off-grid journey is crucial, as budgeting ensures resources are available for necessary infrastructure.
Maintenance and Repairs
Maintenance and repairs pose ongoing challenges for off-grid living. Systems like solar energy and water collection require regular inspections and upkeep. Battery replacement typically occurs every five to fifteen years, depending on the type used. Water filtration systems also demand periodic checks to maintain safe water quality. Staying informed about system efficiency helps residents effectively tackle potential problems, ensuring that their resources remain reliable and functional.
Off-grid living represents a transformative lifestyle choice that prioritizes sustainability and self-sufficiency. By embracing renewable energy sources and eco-friendly practices, individuals can significantly reduce their environmental impact while enjoying the freedom of independent living.
The journey to off-grid living may come with challenges such as initial costs and maintenance requirements. However, the long-term benefits of financial savings and enhanced quality of life make it a compelling option for those seeking to reconnect with nature.
As technology continues to evolve, off-grid homes are becoming increasingly accessible, allowing more people to experience the joys of sustainable living. Embracing this lifestyle not only fosters personal empowerment but also contributes to a healthier planet for generations to come.